 |
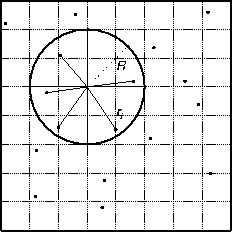
The GMT program nearneighbor implements a simple ``nearest neighbor'' averaging operation. It is the preferred way to grid data when the data density is high. nearneighbor is a local procedure which means it will only consider the control data that is close to the desired output grid node. Only data points inside a search radius will be used, and we may also impose the condition that each of the n sectors must have at least one data point in order to assign the nodal value. The nodal value is computed as a weighted average of the nearest data point per sector inside the search radius, with each point weighted according to its distance from the node as follows:
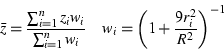
The most important switches are listed in Table 3.2.
|
We will grid the data in the file ship.xyz which contains ship observations of bathymetry off Baja California. We desire to make a 5' by 5' grid. Running minmax on the file yields
ship.xyz: N = 82970 <245/254.705> <20/29.99131> <-7708/-9>
so we choose the region accordingly:
nearneighbor –-R245/255/20/30 –-I5m -–S40k –-Gship.grd –-V ship.xyz
We may get a view of the contour map using
grdcontour ship.grd –-JM6i –-P –-B2 -–C250 –-A1000 | ghostview -